Introduction
In this tutorial, we will discuss NetworkManager command line tool, aka nmcli, in CentOS / RHEL 7. Users who are using ifconfig should avoid this command in Centos 7.
Lets configure some networking settings with nmcli utility.
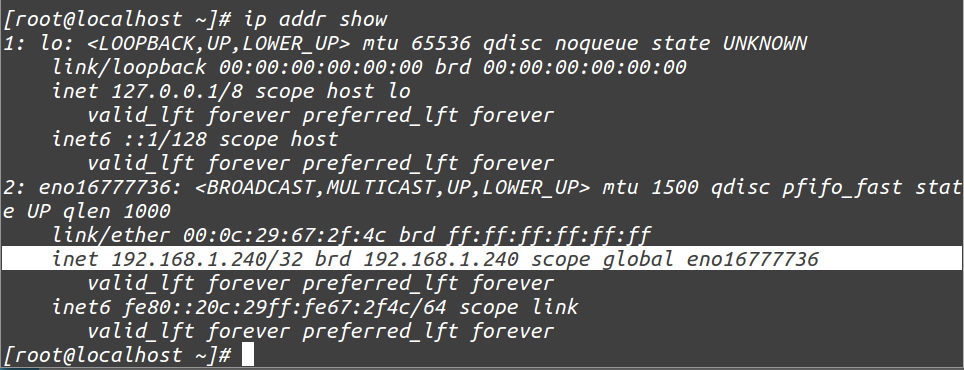
To get all address information of all interfaces connected with System
[root@localhost ~]# ip addr show
Sample Output:
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: eno16777736: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000 link/ether 00:0c:29:67:2f:4c brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 192.168.1.51/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global eno16777736 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:fe67:2f4c/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
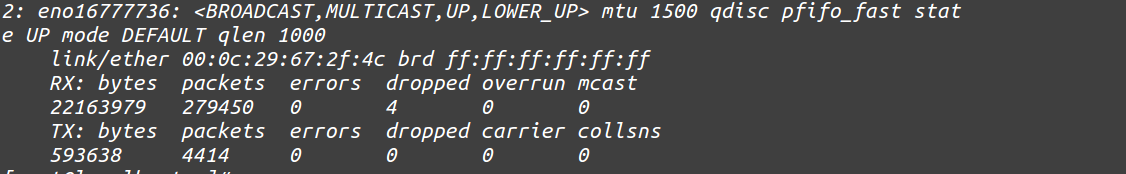
To retrieve packets statistics related with connected interfaces
[root@localhost ~]# ip -s link show eno16777736
Sample Output:
Get routing configuration
[root@localhost ~]# ip route
Sample Output:
default via 192.168.1.1 dev eno16777736 proto static metric 100 192.168.1.0/24 dev eno16777736 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.1.51 metric 100
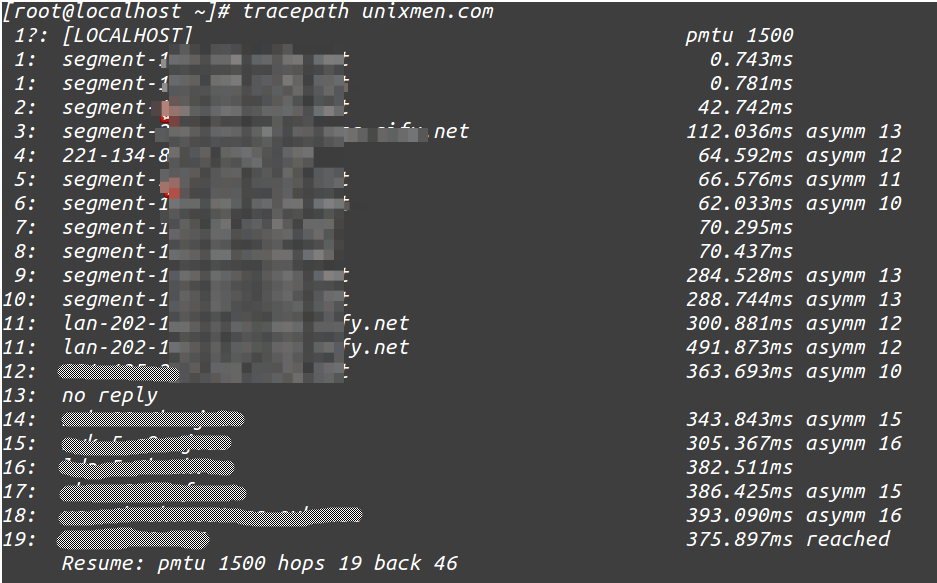
Analyze path for some host/website
[root@localhost ~]# tracepath unixmen.com
Output will be just like traceroute but in more managed form.
nmcli utility
Nmcli is a very rich and flexible command line utility. some of the terms used in nmcli are:
- Device – A network interface being used.
- Connection – A set of configuration settings, for a single device you can have multiple connections, you can switch between connections.
Find out how many connections are available for how many devices
[root@localhost ~]# nmcli connection show
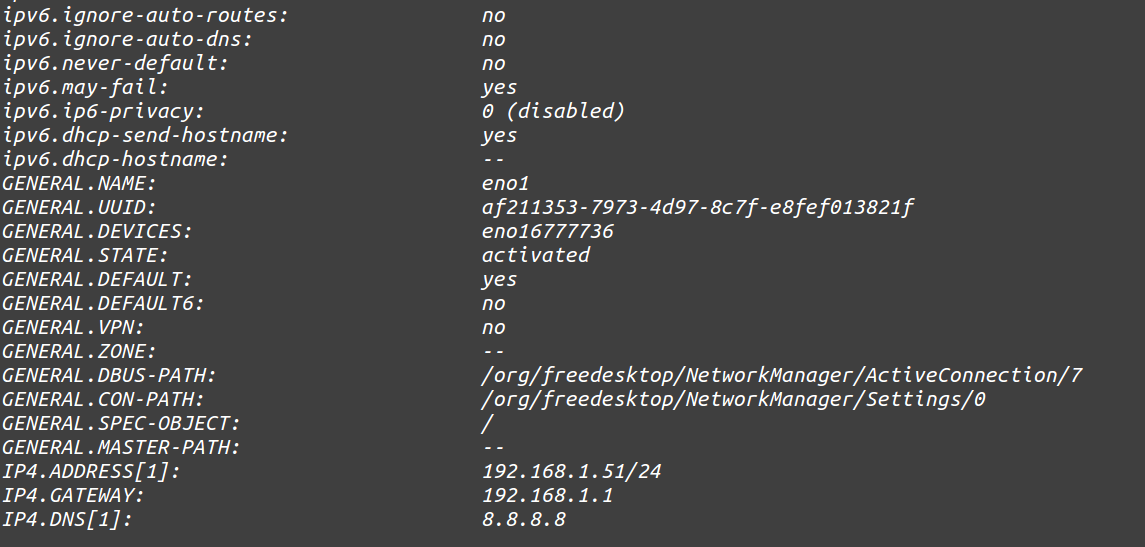
Get details of a specific connection
[root@localhost ~]# nmcli connection show eno1
Sample output:
Get the Network device status
[root@localhost ~]# nmcli device status
DEVICE TYPE STATE CONNECTION eno16777736 ethernet connected eno1 lo loopback unmanaged --
Create a new connection with “dhcp”
[root@localhost ~]# nmcli connection add con-name "dhcp" type ethernet ifname eno16777736
Where,
- Connection add – To add new connection
- con-name – connection name
- type – type of device
- ifname – interface name
This command will add connection with dhcp protocol.
Sample output:
Connection 'dhcp' (163a6822-cd50-4d23-bb42-8b774aeab9cb) successfully added.
Instead of assigning an IP via dhcp, you can add ip address as “static”
[root@localhost ~]# nmcli connection add con-name "static" ifname eno16777736 autoconnect no type ethernet ip4 192.168.1.240 gw4 192.168.1.1
Sample Output:
Connection 'static' (8e69d847-03d7-47c7-8623-bb112f5cc842) successfully added.
Update connection:
[root@localhost ~]# nmcli connection up eno1
Again Check, whether ip address is changed or not.
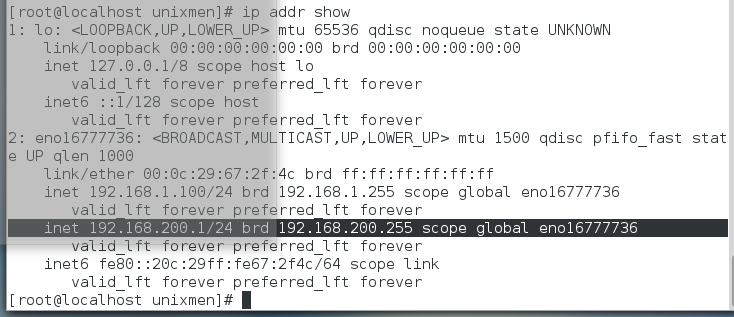
[root@localhost ~]# ip addr show
Add DNS settings to Static connections.
[root@localhost ~]# nmcli connection modify "static" ipv4.dns 202.131.124.4
Add additional DNS value.
[root@localhost ~]# nmcli connection modify "static" +ipv4.dns 8.8.8.8
Note: For additional entries + symbol will be used and +ipv4.dns will be used instead on ip4.dns
Put an additional ip address:
[root@localhost ~]# nmcli connection modify "static" +ipv4.addresses 192.168.200.1/24
Refresh settings using command:
[root@localhost ~]# nmcli connection up eno1
You will see, setting are effective now.
That’s it.