The wait is over. Fedora 23 final edition was released yesterday and while new users can simply download, install and play it, those running Fedora 22 Server or workstation may want to upgrade their systems.
Fedora up-gradation task is really easy. This tutorial describes how to upgrade to Fedora 23 from Fedora 22.
Can’t wait to try the new Fedora? just skip this guide and click the links given below to download Fedora 23 final edition.
The Fedora spins have also been released along with the official release. Spins are alternative desktop environments for Fedora, including KDE, Xfce, LXDE, MATE-Compiz, and SOAS (Sugar on a Stick).
- Get Fedora 23 Workstation
- Get Fedora 23 Server
- Get Fedora 23 Cloud
- Get Fedora 23 Spins
- Get Fedora 23 Labs
Like its predecessors, Fedora 23 comes as three different editions, Fedora 23 workstation, Fedora 23 Server, and Fedora 23 Cloud, targeted to different segment. As the name of each edition implies, each edition comes with respective packages for the particular segment.
Fedora 23 Workstation targets to desktop and laptop users, and Server edition targets to the server, virtualization and storage section, and the Cloud edition targets to the Cloud environment.
What’s new in Fedora 23?
Here is the list of new changes and feature updates in Fedora 23.
- Linux Kernel 4.2;
- GNOME 3.18 ;
- systemd 209 ;
- Mesa 11.0-rc2 ;
- Mono stack 4 ;
-
LibreOffice 5 ;
- LLVM 3.6.1 ;
- GCC 5.1.1 ;
- Updated DNF package manager ;
- Perl 5.22 ;
- Python 3 ;
- SSL3 and RC4 has been disabled by default ;
- Unicode 8.0 ;
- Docker 1.8 ;
- Fedup tool has been removed ;
- And many new improved features.
For more details, check the Fedora 23 release notes.
Upgrade to Fedora 23 From Fedora 22
Well, now let us see how to upgrade from Fedora 22 to 23.
Step 1: Update your system
Log in as root user and install Screen software. The screen tool will help you to reconnect to your server, in case you’re disconnected from it while upgrading.
dnf install screen
Then, start screen session using command:
screen
If you’re disconnected from your Fedora system, you can re-connect to it using command:
screen -Dr
Well, now let us dive into Fedora upgrade task.
Here is my current system (Fedora 22) system details. Execute all commands with root privileges.
cat /etc/redhat-release
Sample output:
Fedora release 22 (Twenty Two)
Or,
cat /etc/*-release
Sample output:
Fedora release 22 (Twenty Two) NAME=Fedora VERSION="22 (Twenty Two)" ID=fedora VERSION_ID=22 PRETTY_NAME="Fedora 22 (Twenty Two)" ANSI_COLOR="0;34" CPE_NAME="cpe:/o:fedoraproject:fedora:22" HOME_URL="https://fedoraproject.org/" BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugzilla.redhat.com/" REDHAT_BUGZILLA_PRODUCT="Fedora" REDHAT_BUGZILLA_PRODUCT_VERSION=22 REDHAT_SUPPORT_PRODUCT="Fedora" REDHAT_SUPPORT_PRODUCT_VERSION=22 PRIVACY_POLICY_URL=https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Legal:PrivacyPolicy VARIANT="Server Edition" VARIANT_ID=server Fedora release 22 (Twenty Two) Fedora release 22 (Twenty Two)
Update your system using the following command:
dnf update
Reboot your system to apply the changes.
Step 2: Start Upgrade
Fedup, the Fedora updater, has been replaced by ‘dnf’ in Fedora 23. fedup is being redesigned and integrated into DNF. For more details, visit here.
Enter the following command to upgrade your Fedora system:
dnf upgrade
Then, install DNF plugin with command:
dnf install dnf-plugin-system-upgrade
Finally, upgrade Fedora 22 to 23 using the following command:
dnf system-upgrade download --releasever=23
The DNF will start to fetch the latest packages. This will take quite a long time depending upon your Internet connection speed. So be patient.
Note:
- If some of your packages have unsatisfied dependencies, the upgrade will refuse to continue until you run it again with an extra –allowerasing option. This often happens with packages installed from third-party repositories for which an updated repositories hasn’t been yet published. Please study very careful the output and examine which packages are going to be removed. None of them should be essential for system functionality, but some of them might be important for your productivity.
- In case of unsatisfied dependencies, you can see more details if you add –best option to the command line.
Once the above command finishes downloading all latest packages, your system will be ready for rebooting.
To boot your system into the upgrade process, run the following command from the Terminal:
dnf system-upgrade reboot
The upgrade will start now.
After completing the upgrade process, the system will automatically reboot.
Select Fedora 23 from the boot menu.
Congratulations! We’re done!. Our Fedora system has been upgraded to the current release i,e Fedora 23 Final.
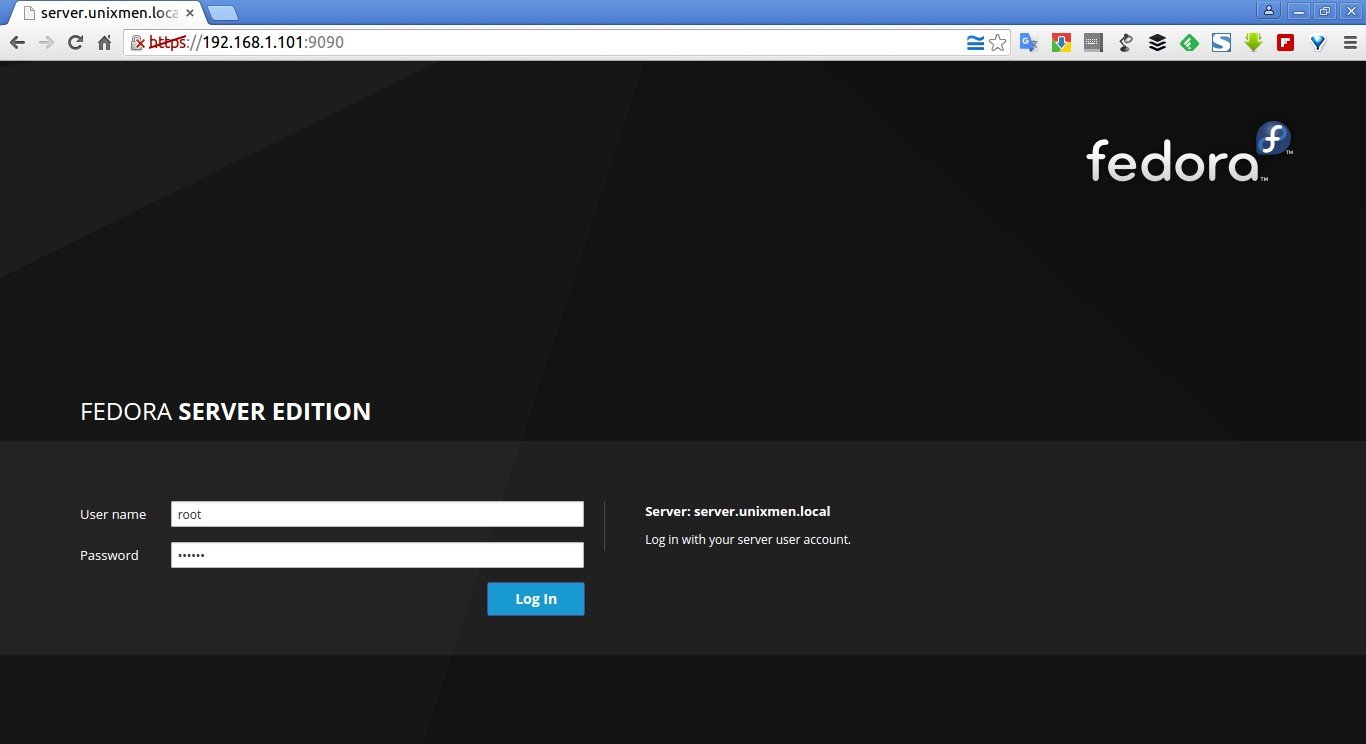
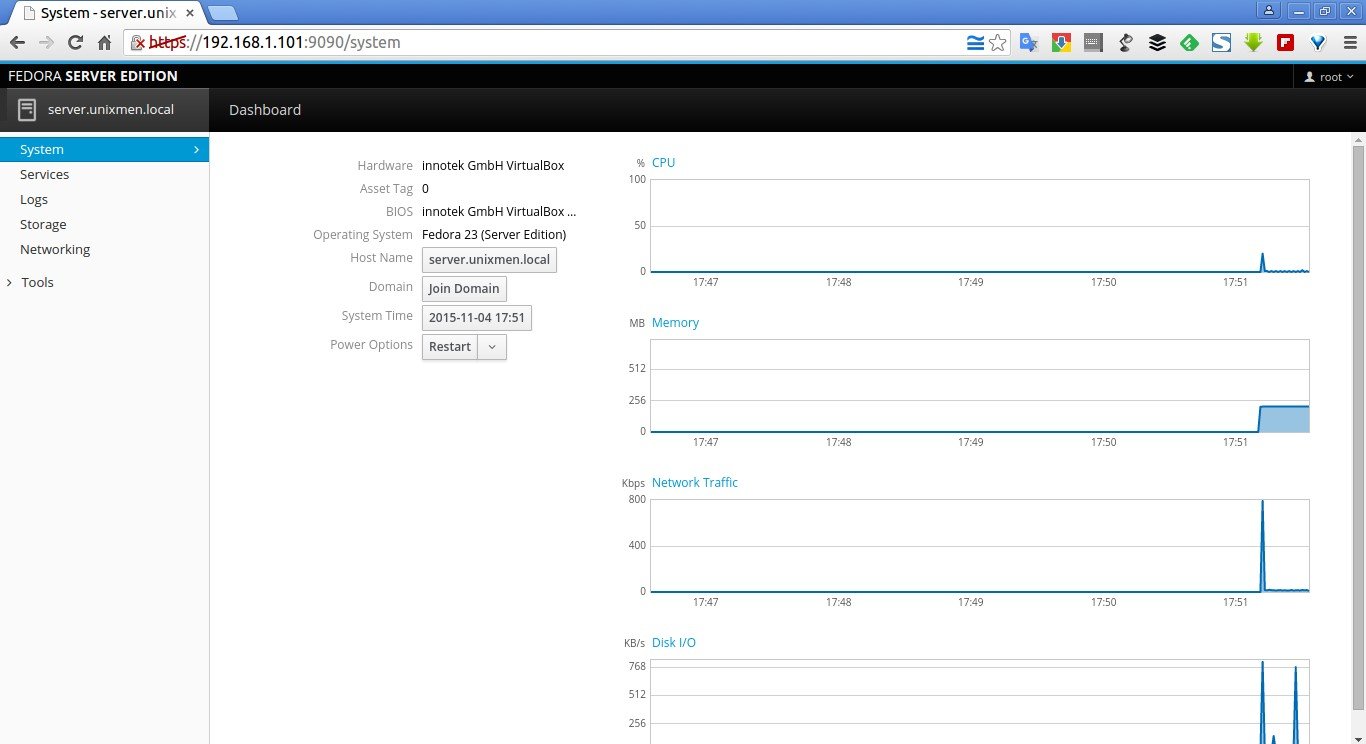
As you see in the above screenshot, Fedora 23 ships with preinstalled web based administration tool called Cockpit in its Server edition by default. So that you can manage it directly via web browser. How cool, isn’t it?
To access the Fedora admin console, open up your web browser and navigate to: https://ip-address:9090. The following screen should appear. Log in using your root user.
Here it is how my Fedora Cockpit admin console looks like.
For more details about Cockpit, please refer the following link.
Now, let us login to our Fedora 23 server and check the version using the following command:
cat /etc/redhat-release
Sample output:
Fedora release 23 (Twenty Three)
Or,
cat /etc/*-release
Sample output:
Fedora release 23 (Twenty Three) NAME=Fedora VERSION="23 (Server Edition)" ID=fedora VERSION_ID=23 PRETTY_NAME="Fedora 23 (Server Edition)" ANSI_COLOR="0;34" CPE_NAME="cpe:/o:fedoraproject:fedora:23" HOME_URL="https://fedoraproject.org/" BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugzilla.redhat.com/" REDHAT_BUGZILLA_PRODUCT="Fedora" REDHAT_BUGZILLA_PRODUCT_VERSION=23 REDHAT_SUPPORT_PRODUCT="Fedora" REDHAT_SUPPORT_PRODUCT_VERSION=23 PRIVACY_POLICY_URL=https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Legal:PrivacyPolicy VARIANT="Server Edition" VARIANT_ID=server Fedora release 23 (Twenty Three) Fedora release 23 (Twenty Three)
That’s it. Start using your new Fedora system.
Any issues after upgrading to Fedora 23?
First see Common F23 bugs or Common F24 bugs to check if the problem is a very prominent issue. If it is not there, search for an existing bug report. If you do not see a report that matches your symptoms, you can file a new report from the search page.
If you hit issues after upgrade with a specific package, file a bug against the package with which you are having issues.
For tips on reporting a bug effectively, read “how to file a bug report.”
Cheers!!
Reference:


![[screen 0: root@server:~] _002](http://unixmen.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/screen-0-root@server-_002.jpg)
![[screen 0: root@server:~] _001](http://unixmen.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/screen-0-root@server-_001.jpg)
![Fedora 22 [Running] - Oracle VM VirtualBox_002](http://unixmen.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/Fedora-22-Running-Oracle-VM-VirtualBox_002.jpg)
![Fedora 22 [Running] - Oracle VM VirtualBox_003](http://unixmen.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/Fedora-22-Running-Oracle-VM-VirtualBox_003.jpg)
![Fedora 22 [Running] - Oracle VM VirtualBox_004](http://unixmen.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/Fedora-22-Running-Oracle-VM-VirtualBox_004.jpg)
![Fedora 22 [Running] - Oracle VM VirtualBox_005](http://unixmen.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/Fedora-22-Running-Oracle-VM-VirtualBox_005.jpg)