LAMP is a combination of operating system and open-source software stack. The acronym LAMP came from the first letters of Linux, Apache HTTP Server, MySQL or MariaDB database, and PHP/Perl/Python.
This tutorial describes how to install LAMP stack on Debian 8 64 bit server. The same steps will work on Debian 7 and all previous versions.
Install LAMP Stack On Debian
1. Install Apache
Apache is an open-source multi-platform web server. It provides a full range of web server features including CGI, SSL and virtual domains.
Switch to root user using command:
su
Then, install Apache web server using the following command:
apt-get install apache2
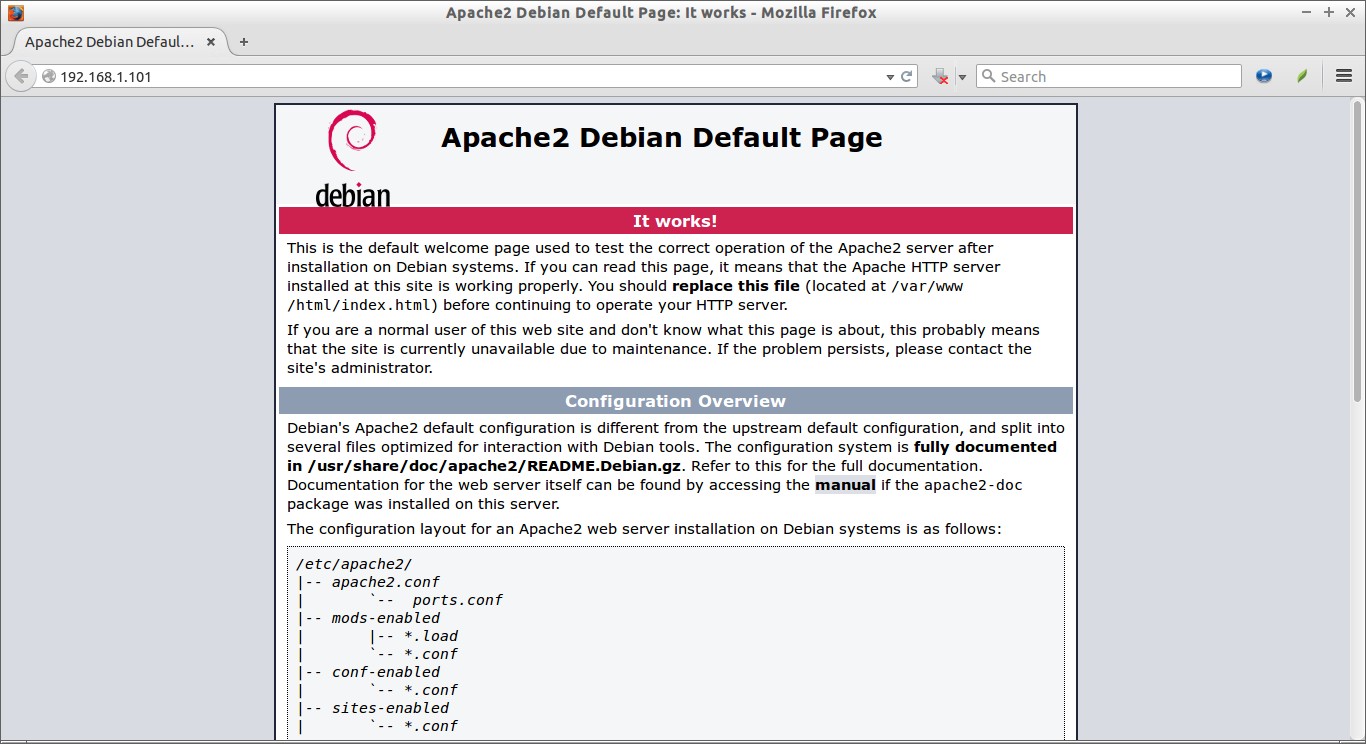
Test Apache:
Open your web browser and navigate to http://localhost/ or http://server-ip-address/.
Voila! Apache web server is working!!
2. Install MySQL
MySQL is a relational database management system (RDBMS) that runs as a server providing multi-user access to a number of databases, though SQLite probably has more total embedded deployments
apt-get install mysql-server mysql-client
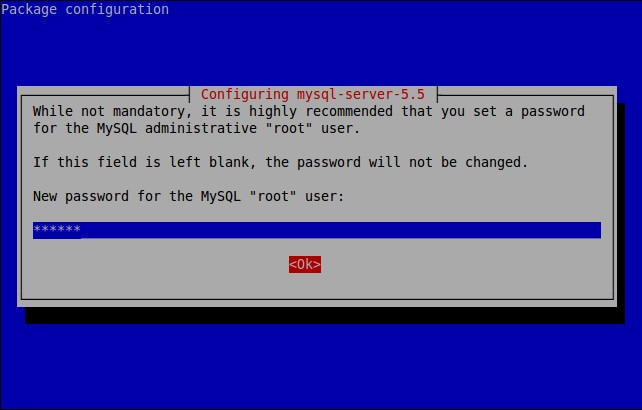
During installation, you’ll be asked to setup the MySQL “root” user password. Enter the password and click Ok.
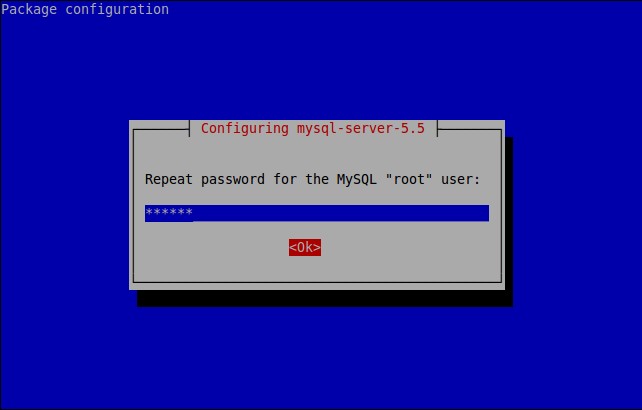
Re-enter the password.
MySQL is installed now.
You can verify the MySQL server status using command:
On Debian 8:
systemctl status mysql
On Debian 7 and previous versions:
service mysql status
Sample output:
● mysql.service - LSB: Start and stop the mysql database server daemon Loaded: loaded (/etc/init.d/mysql) Active: active (running) since Tue 2015-06-23 17:02:44 IST; 20s ago CGroup: /system.slice/mysql.service ├─4605 /bin/sh /usr/bin/mysqld_safe └─4952 /usr/sbin/mysqld --basedir=/usr --datadir=/var/lib/mysql --... Jun 23 17:02:46 debian /etc/mysql/debian-start[5011]: mysql.help_keyword ... Jun 23 17:02:46 debian /etc/mysql/debian-start[5011]: mysql.help_relation ... Jun 23 17:02:46 debian /etc/mysql/debian-start[5011]: mysql.help_topic ... Jun 23 17:02:46 debian /etc/mysql/debian-start[5011]: mysql.host ... Jun 23 17:02:46 debian /etc/mysql/debian-start[5011]: mysql.ndb_binlog_index ... Jun 23 17:02:46 debian /etc/mysql/debian-start[5011]: mysql.plugin ... Jun 23 17:02:46 debian /etc/mysql/debian-start[5011]: mysql.proc ... Jun 23 17:02:46 debian /etc/mysql/debian-start[5011]: mysql.procs_priv ... Jun 23 17:02:46 debian /etc/mysql/debian-start[5074]: Checking for insecure r... Jun 23 17:02:46 debian /etc/mysql/debian-start[5079]: Triggering myisam-recov... Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full.
3. Install MariaDB
In case you want to use MariaDB instead of MySQL community edition, follow the steps given below.
MariaDB is a drop in replacement for MySQL. It is a robust, scalable and reliable SQL server that comes rich set of enhancements.
First you have to remove existing MySQL packages if any. To completely uninstall MySQL along with its configuration files, enter the following commands one by one:
systemctl stop mysql
Or,
service mysql stop
apt-get remove --purge mysql-server mysql-client mysql-common
apt-get autoremove
apt-get autoclean
rm -rf /var/lib/mysql/
rm -rf /etc/mysql/
After removing MySQL, run the following command to install MariaDB.
apt-get install mariadb-server
Alternatively, you can install it using MariaDB repository if you want to try most recent version of MariaDB. Run the following commands to add PPA.
apt-get install python-software-properties
apt-key adv --recv-keys --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com 0xcbcb082a1bb943db
add-apt-repository 'deb http://kartolo.sby.datautama.net.id/mariadb/repo/10.0/debian jessie main'
Update the software sources list and install MariaDB using following commands:
apt-get update
apt-get install mariadb-server
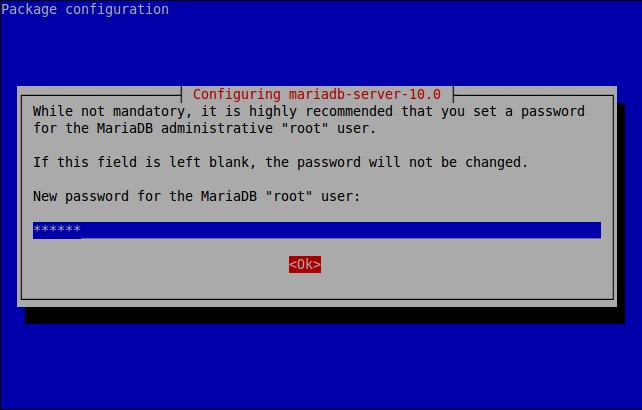
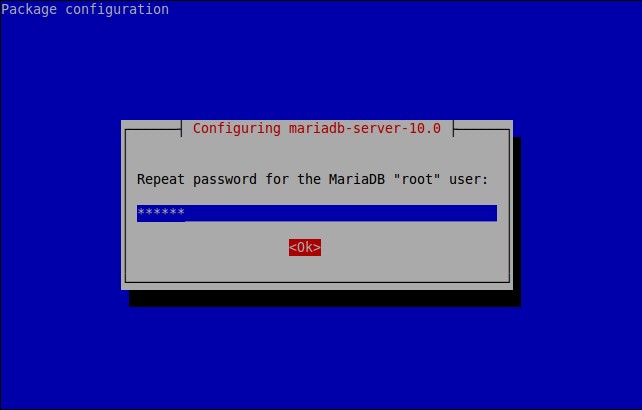
During installation you will be asked to set MariaDB ‘root’ user password. Enter the password twice, and complete the installation.
Re-enter password:
Check if mariadb is running or not, using the following command:
On Debian 8:
systemctl status mysql
On Debian 7 and previous versions:
service mysql status
Sample output:
● mysql.service - LSB: Start and stop the mysql database server daemon Loaded: loaded (/etc/init.d/mysql) Active: active (running) since Tue 2015-06-23 17:36:27 IST; 52s ago CGroup: /system.slice/mysql.service ├─2918 /bin/bash /usr/bin/mysqld_safe ├─2919 logger -p daemon.err -t /etc/init.d/mysql -i └─3060 /usr/sbin/mysqld --basedir=/usr --datadir=/var/lib/mysql --plugin-dir=/usr/lib/mysql/plugin --user=mysql --log-error=/var/log/mysql/error.log --pid... [...] Jun 23 17:36:29 debian /etc/mysql/debian-start[3111]: mysql.time_zone_leap_second OK Jun 23 17:36:29 debian /etc/mysql/debian-start[3111]: mysql.time_zone_name OK Jun 23 17:36:29 debian /etc/mysql/debian-start[3111]: mysql.time_zone_transition OK Jun 23 17:36:29 debian /etc/mysql/debian-start[3111]: mysql.time_zone_transition_type OK Jun 23 17:36:29 debian /etc/mysql/debian-start[3111]: mysql.user OK Jun 23 17:36:29 debian /etc/mysql/debian-start[3180]: Checking for insecure root accounts. Jun 23 17:36:29 debian /etc/mysql/debian-start[3184]: Triggering myisam-recover for all MyISAM tables Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full.
4. Install PHP
PHP (recursive acronym for PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor) is a widely used open-source general purpose scripting language that is especially suited for web development and can be embedded into HTML.
Install PHP with following command:
apt-get install php5 php5-mysql libapache2-mod-php5
To test PHP, create a sample “testphp.php” file in Apache document root folder.
nano /var/www/html/testphp.php
Add the following lines.
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
Restart apache2 service.
On Debian 8:
systemctl restart apache2
On Debian 7 and previous versions:
service apache2 restart
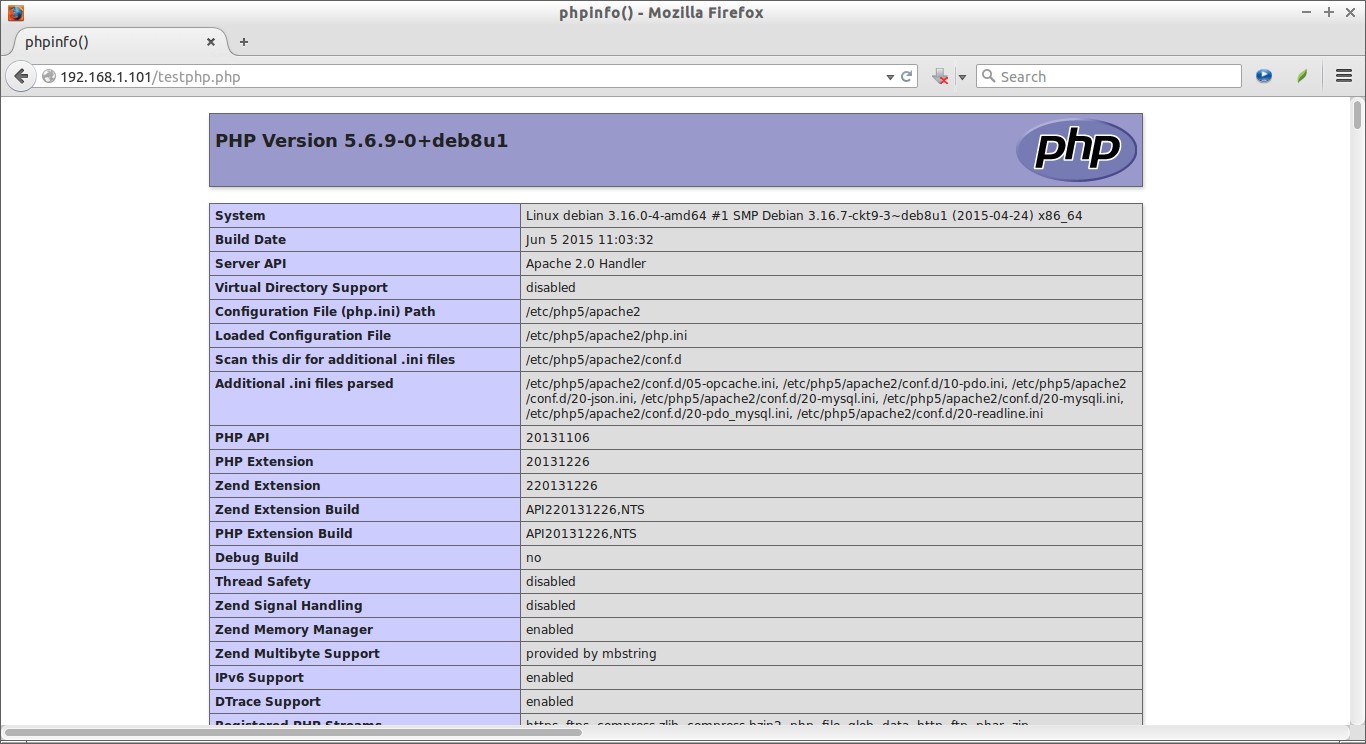
Navigate to http://server-ip-address/testphp.php. It will display all the details about php such as version, build date and commands etc.
If you want to install all php modules at once, enter the command apt-get install php* and restart the apache2 service. To verify the modules, open web browser and navigate to http://server-ip-address/testphp.php. You will able to see all installed php modules.
5. Manage MySQL Databases Using phpMyAdmin (Optional)
phpMyAdmin is a free open-source web interface tool used to manage your MySQL databases.
It is available in the Official Debian repositories.So install it with command:
apt-get install phpmyadmin
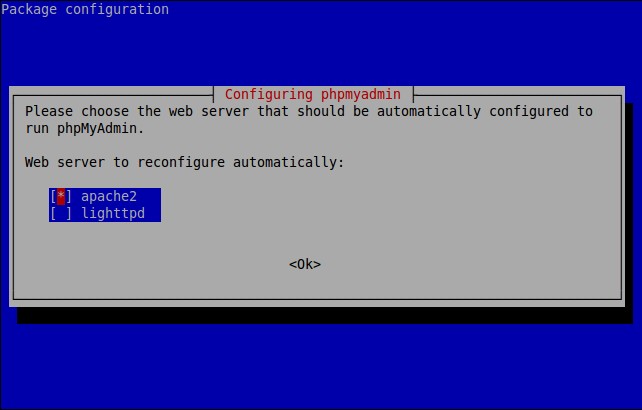
Select the Web server that should be automatically configured to run phpMyAdmin. In my case, it is apache2.
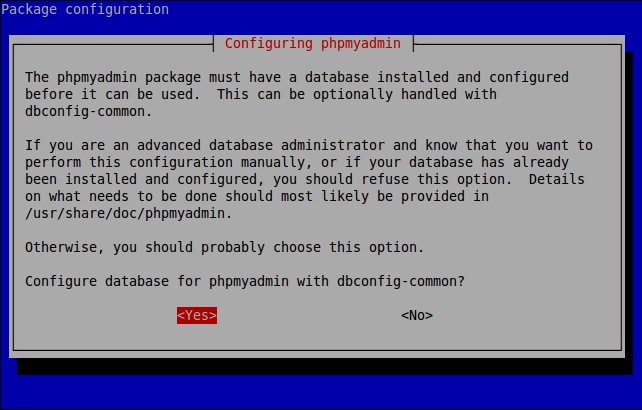
The phpMyAdmin must have a database installed and configured before it can be used. This can be optionally handled by dbconfig-common.
Select ‘Yes’ to configure database for phpmyadmin wjth dbconfig-common.
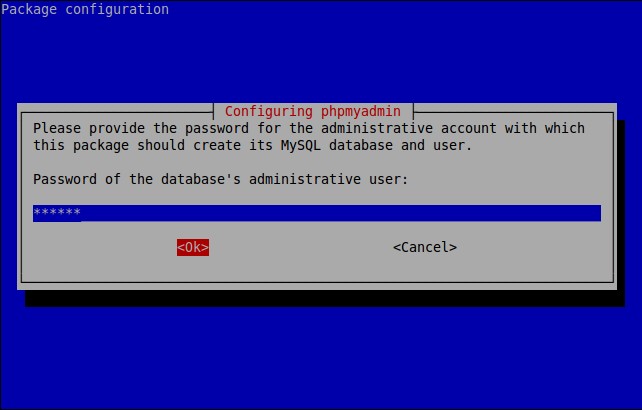
Enter password of the database’s administrative user.
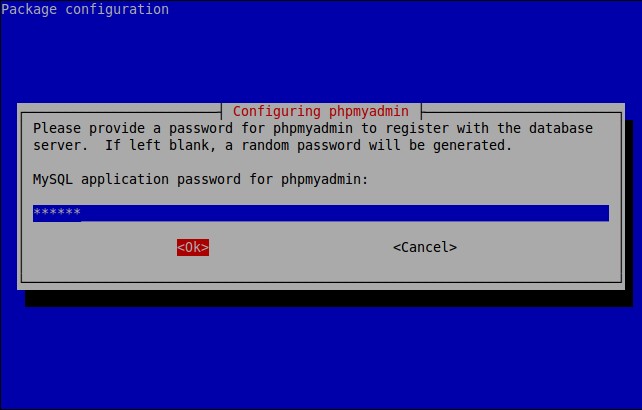
Enter MySQL application password phpmyadmin.
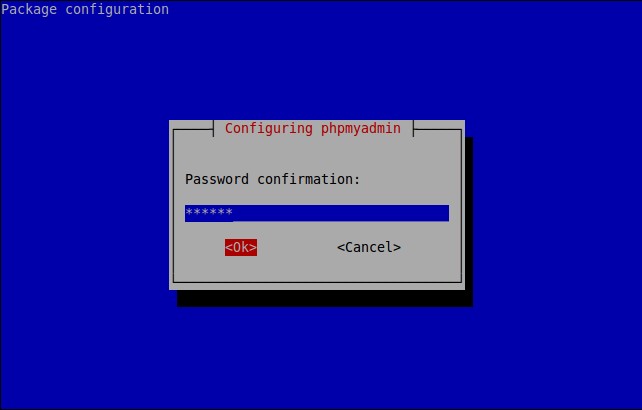
Re-enter the password.
Success! phpMyAdmin installation is installed.
Additional Note: if you followed all steps carefully, phpMyAdmin should work just fine. In case phpMyAdmin is not working, please do the following steps.
Open terminal, and type:
nano /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
Add the following line at the end.
Include /etc/phpmyadmin/apache.conf
Save and Exit. Restart apache service:
On Debian 8:
systemctl restart apache2
On Debian 7 and previous versions:
/etc/init.d/apache2 restart
6. Access phpMyAdmin Web Console
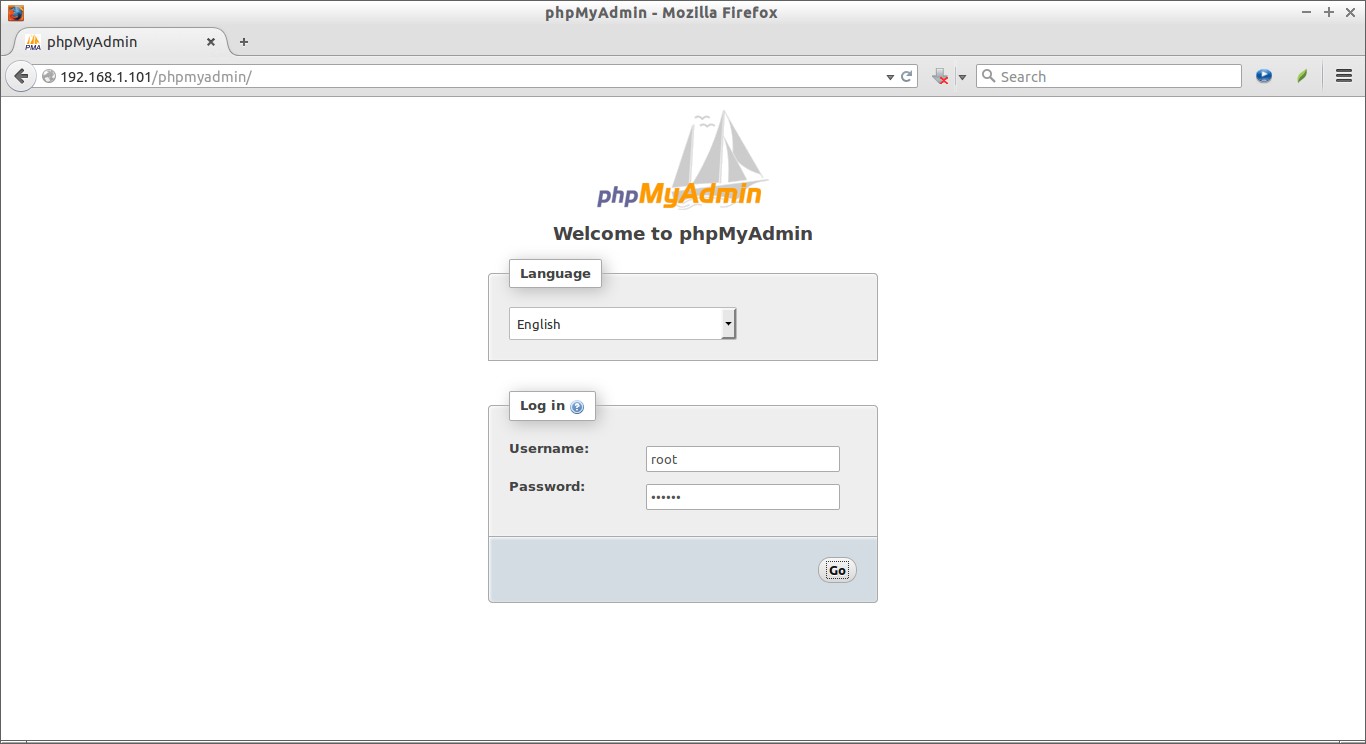
Now, you can access the phpmyadmin console by navigating to http://server-ip-address/phpmyadmin/ from your browser.
Enter your MySQL username and password which you have given in previous steps. In my case its “root” and “debian”.
You will be redirected to PhpMyAdmin main web interface.
From now on, you can manage your MySQL databases from phpMyAdmin web interface.
That’s it. Your LAMP stack is ready to use.