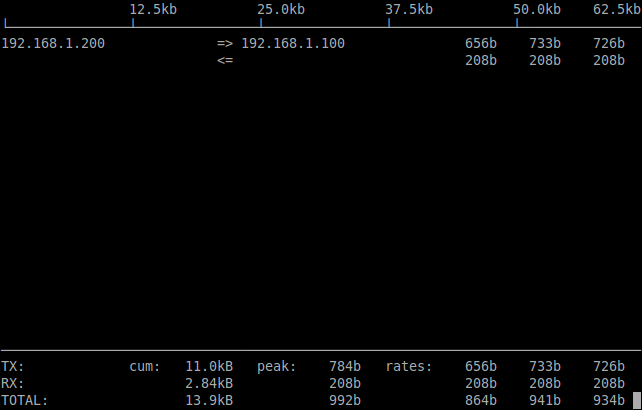
iftop is used to view the current bandwidth on a network interface. It listens to network traffic on a named interface and displays a table of current bandwidth usage by pairs of hosts. iftop must be run by a root user or a user who has sufficient privileges to monitor network bandwidths.
Installing iftop
On Debian/Ubuntu:
sk@sk:~$ sudo apt-get install iftop
On CentOS/RHEL:
iftop will not be found in official repositories. So let us add EPEL repository to install iftop:
[root@server ~]# rpm -ivh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/i386/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
Now install it using the following command:
[root@server ~]# yum install iftop
Usage
iftop is very simple to use. Just type the iftop command on terminal with root privileges to display the bandwidth usage of the first network interface. Press Q to exit from the iftop command output.
[root@server ~]# iftop
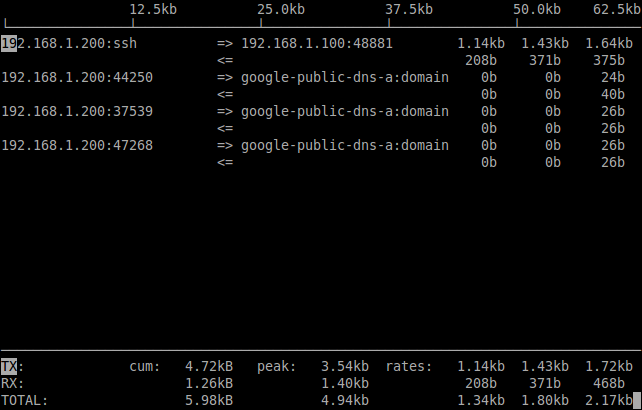
To view the source and destination listening ports, just press SHIFT+S and SHIFT+D. It will display the traffic along with source and destination ports.
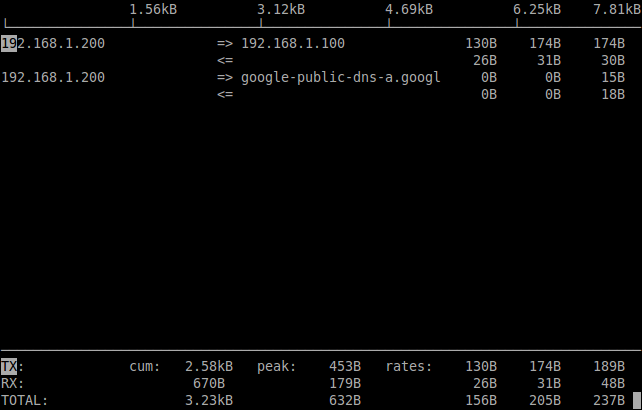
To view the network bandwidth of a particular interface, use the following command.
[root@server ~]# iftop -i eth0
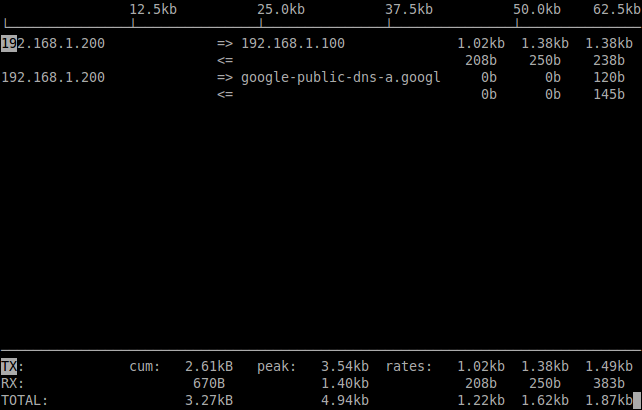
[root@server ~]# iftop -i eth0 -B
[root@server ~]# iftop -i eth0 -P -N
The parameter -N displays the port number.
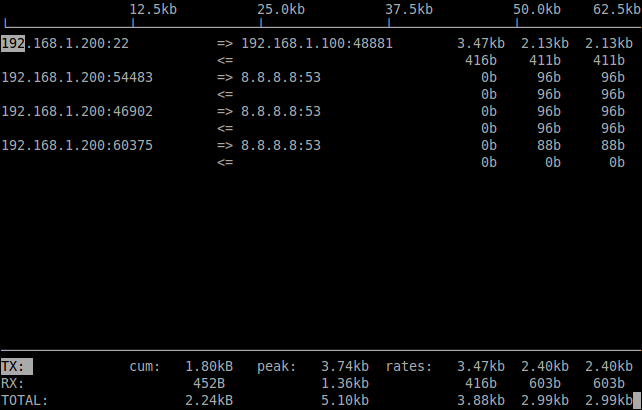
[root@server ~]# iftop -F 192.168.1.0/24
For more information about iftop command, refer the man pages using the following command:
[root@server ~]# man iftop