Introduction
HipHop Virtual Machine (HHVM) is an open-source virtual machine designed for executing programs written in Hack and PHP. It uses a just-in-time compilation to provide better performance and supports PHP 5 and major features of PHP 7. This tutorial explains how to set up and run WordPress with NGINX and HHVM on openSUSE 42.2 Leap.
Getting started
Install NGINX
NGINX is available on openSUSE repositories, so just use
to install it:
Start it with
:
Check if everything is going well using the following code:
# systemctl status nginx
nginx.service - The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; disabled; vendor preset: disab led) Active: active (running) since Mon 2017-03-13 13:49:14 CET; 26s ago
Install and configure MariaDB
As for NGINX, MariaDB is available in repositories. To start:
# zypper in mariadb mariadb-client
Fire it up and verify with
:
# systemctl start mysql # systemctl status mysql
mysql.service - MySQL server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/mysql.service; disabled; vendor preset: disab led) Active: active (running) since Mon 2017-03-13 13:56:27 CET; 5s ago
Configure its root account:
# mysql_secure_installation
New password: Re-enter new password: Password updated successfully! Reloading privilege tables.. ... Success! Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y ... Success! Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] Y ... Success! Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y - Dropping test database... ... Success! - Removing privileges on test database... ... Success! Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y ... Success! Cleaning up... All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB installation should now be secure. Thanks for using MariaDB!
Create new user and database for WordPress. Login to MariaDB shell:
# mysql -u root -p
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE wordpress_db; MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE USER wordpressusr@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'usr_strong_password' ; MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON wordpress_db.* TO wordpressusr@localhost IDENT IFIED BY 'usr_strong_password'; MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES; MariaDB [(none)]> EXIT;
Now, MariaDB is correctly installed and configured, and a new database for WordPress has been created. Take note of its informations.
Install HHVM
To install HHVM, first you must add a repository:
# zypper addrepo http://download.opensuse.org/repositories/home:munix9/openSUSE_Leap_42.2/home:munix9.repo
Then refresh repositories with:
# zypper refresh
Enter ‘a’ to trust the key:
Repository: munix9's Home Project (openSUSE_Leap_42.2) Key Name: home:munix9 OBS Project <home:munix9@build.opensuse.org> Key Fingerprint: 3FE0C0AC 1FD6F103 4B818A14 BDF3F6AC D4D81407 Key Created: Tue Aug 16 11:47:54 2016 Key Expires: Thu Oct 25 11:47:54 2018 Rpm Name: gpg-pubkey-d4d81407-57b2e14a Do you want to reject the key, trust temporarily, or trust always? [r/t/a/? shows all op tions] (r): a Retrieving repository 'munix9's Home Project (openSUSE_Leap_42.2)' metadata ......[done] Building repository 'munix9's Home Project (openSUSE_Leap_42.2)' cache ...........[done]
Now, install HHVM:
# zypper in hhvm hhvm-nginx hhvm-fastcgi
Configure HHVM and NGINX
Create a user and a group named nginx:
# useradd -M -s /bin/bash -U nginx
Next, you’ll need to configure HHVM for running with NGINX as the web server. To do this, edit the following file:
# $EDITOR /etc/hhvm/server.ini
Uncommenting line 3, Unix sockets will be enabled for HHVM. After the modification, the content of the file should look like this:
; some settings already defined in hhvm.service ;hhvm.server.port = 9000 hhvm.server.file_socket = /run/hhvm/server.sock hhvm.server.type = fastcgi hhvm.server.default_document = index.php ; if you use mod_rewrite or get a 404 not found please try adding: ;hhvm.server.fix_path_info = true hhvm.log.use_log_file = true hhvm.log.file = /var/log/hhvm/server.log hhvm.repo.central.path = /var/lib/hhvm/hhvm.hhbc ;hhvm.repo.central.file_mode = 420 ;hhvm.repo.central.file_user = hhvm ;hhvm.repo.central.file_group = hhvm
Next, edit the HHVM service, and change the user in nginx:
# $EDITOR /usr/lib/systemd/system/hhvm.service
[Unit] Description=HipHop Virtual Machine (FCGI) After=syslog.target network.target Before=apache2.service nginx.service [Service] PrivateTmp=true PIDFile=/run/hhvm/server.pid ExecStartPre=/bin/rm -f /run/hhvm/server.sock ExecStart=/usr/bin/hhvm --config /etc/hhvm/php.ini --config /etc/hhvm/server.ini --user nginx --mode server -vServer.Type=fastcgi -vServer.FileSocket=/run/hhvm/server.sock -vPi dFile=/run/hhvm/server.pid [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save, exit, and change the owner of
:
#chown -R nginx:nginx /var/run/hhvm/
Next, configure HHVM to work with NGINX.
First, execute the following command:
# cp /etc/nginx/hhvm.conf.example /etc/nginx/hhvm.conf
Then, edit this configuration file:
# $EDITOR /etc/nginx/hhvm.conf
As follows:
location ~ \.(hh|php)$ {
root /srv/www/htdocs;
fastcgi_keep_conn on;
#fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/hhvm/server.sock;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
Next, edit the NGINX configuration file,
. On line 59, add:
Save, exit, start HHVM and restart NGINX:
# systemctl start hhvm # systemctl restart nginx
Test NGINX:
# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
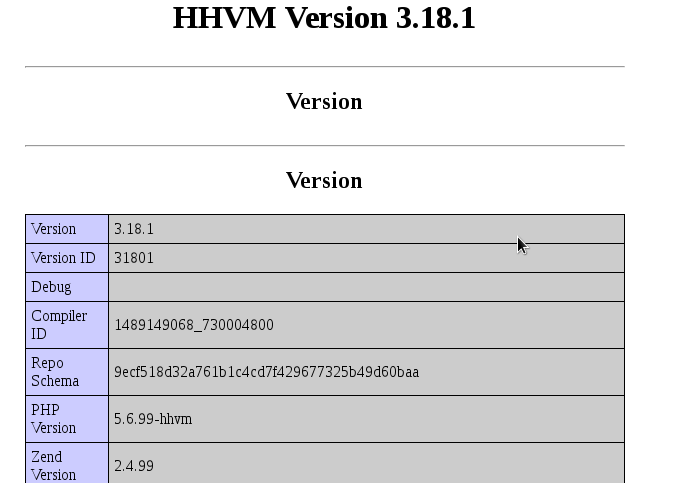
Now test HHVM. To accomplish this task, create a new file called
on
and write the following code into it:
Save and exit. With a web browser, go to http://localhost/info.php and it should display the following page:
Create a new Virtual Host
Now it’s time to create a new Virtual Host file for NGINX that will be stored in the folder
. Create it:
# mkdir -p /etc/nginx/vhosts.d/
Inside it, create a new file:
# $EDITOR /etc/nginx/vhosts.d/mysite.conf
And paste the following configuration:
server {
# This line for redirect non-www to www
server_name mywebsite.co;
rewrite ^(.*) http://www.mywebsite.co$1 permanent;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.mywebsite.co;
root /srv/www/mysite;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root /srv/www/htdocs;
}
# HHVM running throught Unix-Socket
location ~ \.(hh|php)$ {
root /srv/www/mysite;
fastcgi_keep_conn on;
#fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/hhvm/server.sock;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}
Save and exit.
Create the web site root directory, specified in the Virtual Host configuration file:
# mkdir -p /srv/www/mysite
Install WordPress
Download WordPress in the site root directory:
# cd /srv/www/mysite # wget wordpress.org/latest.zip
Next, extract the archive:
# unzip latest.zip # mv wordpress/* .
Copy the sample configuration file and edit it:
# cp wp-config-sample.php wp-config.php # $EDITOR wp-config.php
Edit the database lines as follows:
// ** MySQL settings - You can get this info from your web host ** //
/** The name of the database for WordPress */
define('DB_NAME', 'wordpress_db');
/** MySQL database username */
define('DB_USER', 'wordpressusr');
/** MySQL database password */
define('DB_PASSWORD', 'usr_strong_password');
/** MySQL hostname */
define('DB_HOST', 'localhost');
Save and exit.
Conclusion
Now, just visit with the following URL with a web browser: www.mywebsite.co. WordPress should start, giving you the chance to finish configuration, and start using WP!