As a UNIX user, one of the basic tasks that you will often find yourself performing is renaming files and folders. Renaming a file is quite elementary and really shouldn’t be an uphill task. You can rename a file or directory in UNIX from a terminal (CLI) or using third-party tools (GUI tools).
In this guide, we will discuss two command-line tools that you can use to rename files in UNIX.
Rename files in UNIX using the mv command
Short for ‘move’ the mv command is a command that is used primarily to move files and folder from one location to another. However, it can also be used to rename a file.
The syntax for renaming a file using the mv command is shown below:
$ mv (option) filename1 filename2
In the command above,
Let’s take an example as shown in the command below:
$ mv /home/sales.txt /home/marketing.txt
The command renames the file
NOTE:
When the file is not located in the current folder, the complete file path to the file and the new file name should be specified. If the path of the file differs from the path of the new filename, the file will be moved to the new file path and later on renamed.
For example:
$ mv /home/sales.txt /home/data/marketing.txt
In the above example, the
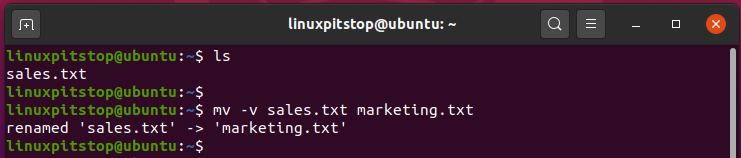
The mv command can be used with a variety of options. For example to print the verbose output of the command, use the
$ mv -v sales.txt marketing.txt
Renaming a directory
Renaming a directory also follows the same syntax as renaming a file, i.e.
$ mv directory_name1 directory_name2
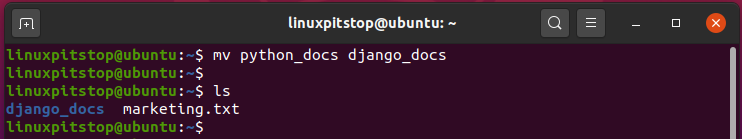
For example, to rename a directory called
$ mv python_docs django_docs
Rename files in UNIX using the rename command
So far we have looked at how to rename files and directories using the
This is where the
Installing rename
Modern Linux distributions ship with rename command by default. However, if you are running an older Linux distribution, here is how you to install it:
For Debian and Ubuntu systems, run the command:
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt-get install rename
For CentOS, Fedora and RHEL, execute:
$ sudo dnf install prename
Notice the ‘p’ that precedes the rename command. The ‘p’ stands for Perl.
For Arch / Manjaro systems run:
$ sudo pacman -Syu perl-rename
Using rename command
As earlier stated, the rename command is used for renaming a batch of files, more specifically changing the file extension of multiple files simultaneously.
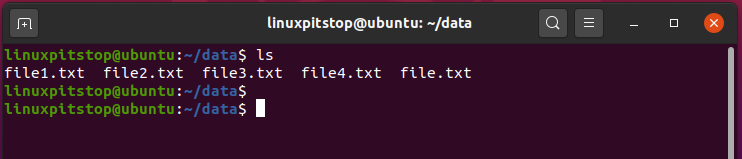
To better demonstrate how the command works, we have 5 text files all with a ‘.txt’ file extension as shown.
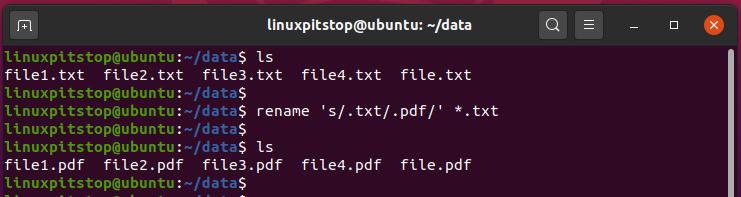
The following command is going to convert all the .txt files to .pdf files
$ rename 's/.txt/.pdf/' *.txt
You can confirm that the files have been renamed using the good-old
Let’s break down the command:
‘s/…/…/’ – This is the substitution operator. The first argument is the search term and the second argument is the replacement.
.txt – This represents the search term. The rename command will scour for this pattern in all files in the directory and thereafter replace it with the second argument
.pdf – This is the replacement option that will replace the pattern in the first argument.
*.txt – The use of the wildcard symbol instructs the rename command to search for all instances with the pattern .txt
If you are not sure which files will be affected, you might need to perform a dry run before proceeding with the operation.
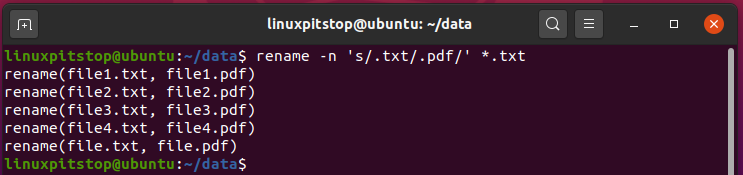
To achieve this, use the -n option as shown
$ rename -n 's/.txt/.pdf/' *.txt
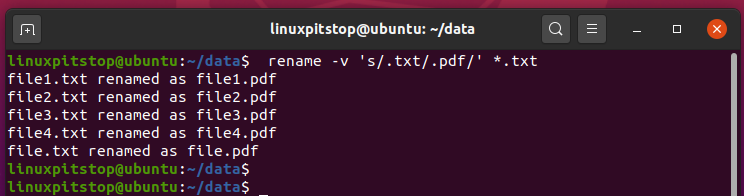
To view the verbose output as files are being renamed, use the -v option as shown.
$ rename -v 's/.txt/.pdf/' *.txt
And this brings us to the end of this topic on how to rename files in UNIX. Renaming files is part of the basic commands that every Linux user should have at their fingertips. We hope that you can comfortably rename your files and directories without much of an issue. Give us a shout and let us know if you are having any difficulties.





