Understanding Dockers
Docker is an emerging technology; it lets you automate the deployment of your applications within container environment. It is highly efficient to run your applications inside docker containers as compared to virtual machines and stand alone servers. Dockers make it easy to deploy, backup and ship your applications. Simply package and distribute your application along with its dependencies using a docker container; it’s easy, portable, lightweight way.
Understanding Docker Hub
Docker registry is a service that lets you easily share your created docker images. Once you develop your application and pack it into a docker image, you need docker registry service to distribute it among your users all around the world. Docker Hub is an online, free docker registry service, simply create a free account and start using it. It gives you good control over your docker images. You can choose your images to be shared with public or keep it private for your own use.
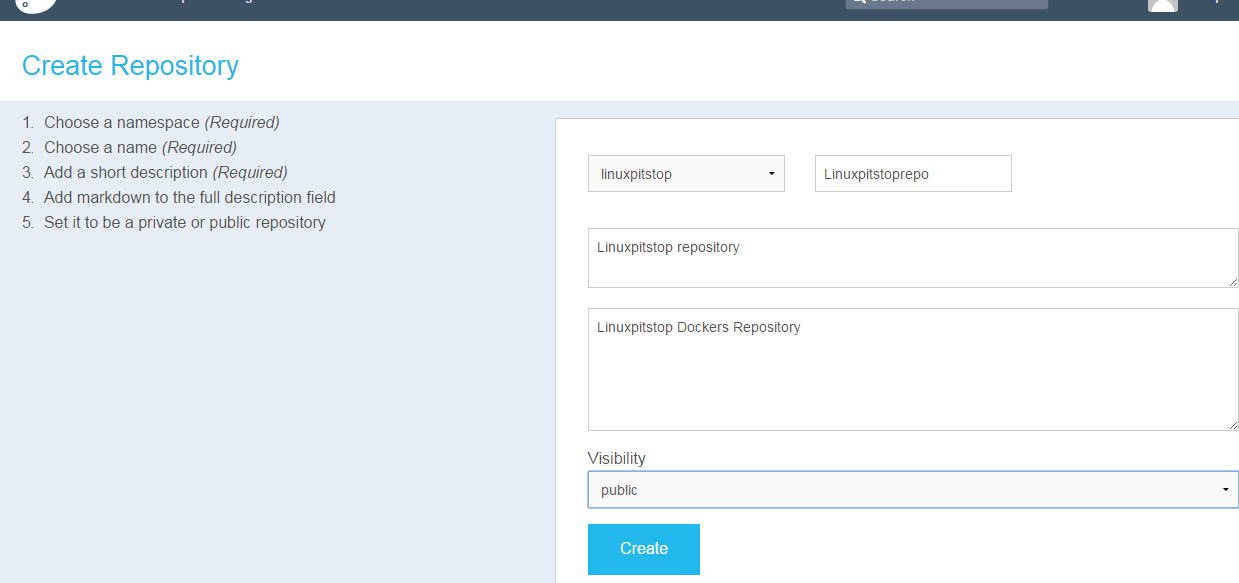
In order to create an account on Docker Hub, visit it here and provide your email account, username and password. Once account has been created, add a repository by providing repository name, details and “Visibility”.
Backup and upload Docker Image to Docker Hub
Let’s see how we can backup our docker containers and upload the created backup to docker hub for distribution purposes. Launch your system terminal and run following command to see your docker container’s list.
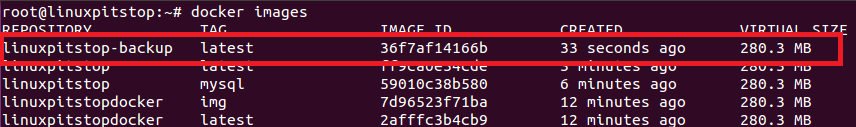
It should output as shown in the following screenshot. If you have more than one containers , it will list all, simply note down the “Container ID” from here for the container you want to backup.
Once we have Container ID, we can backup the container as image by running the “commit” command in the following syntax.
Replace “CONTAINERID” with your container ID and “BACKUPNAME” with the name you want to give to backup image.
ff9ca0e54cde7354153df3b9a6ca2a3755fda1df63e836e3fe971603a20b515a
Now run following command to verify that your container’s backup has been generated.
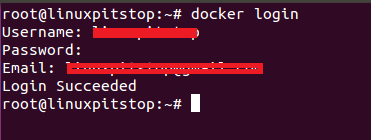
Now login your Docker Hub account by running the following command and providing your username, password and email account.
Create a tag for your docker image here by running the following command.
Replace IMAGE-ID with the ID of your docker image and TAG-NAME with the name you want to give.
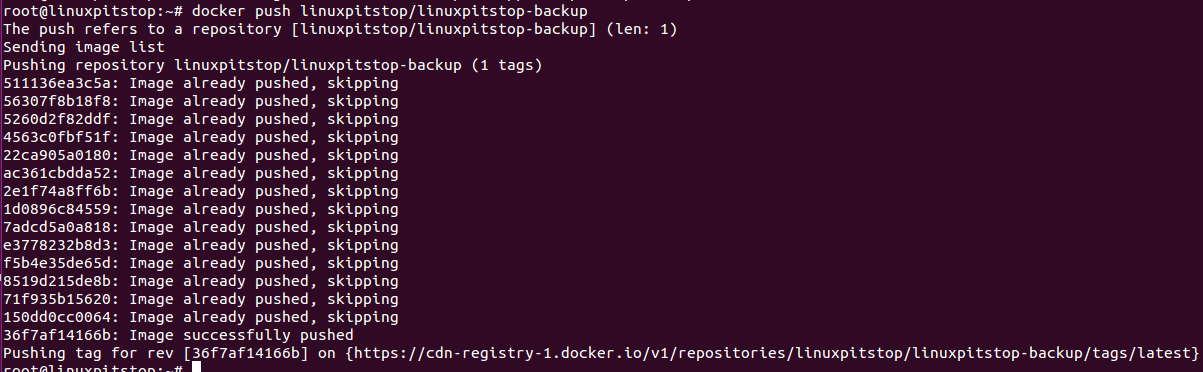
Now run following command to successfully complete the upload process.
There you go, your docker image is ready for distribution now, you can explore your Docker Hub account and can see it there.
Conclusion
Docker is an evolving technology and getting massive popularity. System administrators and developers are using it for the successful deployment of their applications, it has proven advantages over other available alternate technologies. If you haven’t created your first docker container yet, do it today; you will enjoy working with this amazing idea.