Darkstat is a simple, web based network traffic analyzer application. It works on many popular operating systems like Linux, Solaris, Mac and AIX. It keeps running in the background as a daemon and continues collecting and sniffing network data and presents it in easily understandable format within its web interface. It can generate traffic reports for hosts, identify which ports are open on some particular host and is IPV 6 complaint application. Let’s see how we can install and configure it on Linux operating system.
Installing Darkstat on Linux
Install Darkstat on Fedora/CentOS/RHEL:
In order to install it on Fedora/RHEL and CentOS Linux distributions, run following command on the terminal.
Install Darkstat on Ubuntu/Debian:
Run following on the terminal to install it on Ubuntu and Debian.
Congratulations, Darkstat has been installed on your Linux system now.
Configuring Darkstat
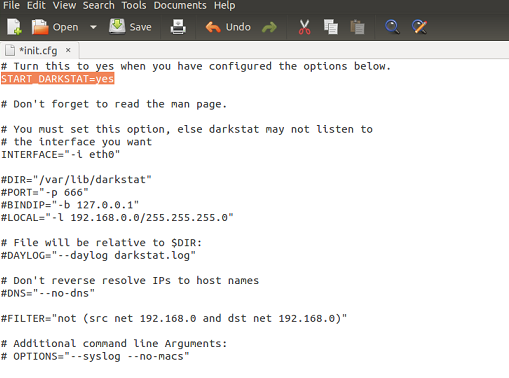
In order to run this application properly, we need to perform some basic configurations. Edit /etc/darkstat/init.cfg file in Gedit text editor by running the following command on the terminal.
Change START_DARKSTAT parameter to “yes” and provide your network interface in “INTERFACE”. Make sure to uncomment DIR, PORT, BINDIP, and LOCAL parameters here. If you wish to bind the web interface for Darkstat to some specific IP, provide it in BINDIP section.
Starting Darkstat Daemon
Once the installation and configuration for Darkstat is complete, run following command to start its daemon.
You can configure Darkstat to start on system boot by running the following command:
Launch your browser and load http://localhost:666 and it will display the web based graphical interface for Darkstat. Start using this tool to analyze your network traffic.
Conclusion
It is a lightweight tool with very low memory footprints. The key reason for the popularity of this tool is simplicity, ease of configuration and usage. It is a must-have application for System and Network Administrators.