Introduction
Apache Tomcat is a Java Servlet Container which implements several Java EE specifications including JavaServer Pages (JSP), Java Servlet, WebSocket and Java EL. It also provides an HTTP web server environment in which Java code can run. It’s distributed under the Apache License 2.0.
This tutorial explains how to install and configure Tomcat 8.5.11 on Debian 8.
Getting started
Install Java
The first thing to do is to install
, for managing repository:
# apt install python-software-properties -y
Next, add required repository:
# echo "deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/webupd8team/java/ubuntu xenial main" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/webupd8team-java.list # echo "deb-src http://ppa.launchpad.net/webupd8team/java/ubuntu xenial main" | tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/webupd8team-java.list # apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv-keys EEA14886 # apt update
Now, you can install Java:
# apt install oracle-java8-installer -y
Accept the licence, and then wait for the installation process to complete. Next, check Java version:
# java -version
just to be sure that everything went well.
Configure JAVA_HOME
Now you need to configure the environment variable (JAVA_HOME) on the server:
# update-alternatives --config java
You should see the following Java path: /usr/lib/jvm/java-8-oracle/jre/bin/java
Edit the environment file
, adding the following line:
Save and exit.
Next, edit
writing the lines:
JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-oracle/jre export JAVA_HOME PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH export PATH
Save, exit and reload the file:
# source ~/.bashrc
Now, executing the command:
# echo $JAVA_HOME
you should read the correct path to Java.
Install Tomcat
Once you have configured Java, it’s time to install Apache Tomcat. For that, we will use a “tomcat” as the user and group:
# groupadd tomcat # useradd -s /bin/false -g tomcat -d /opt/tomcat tomcat
With this command we created a user named tomcat, which uses
as the home directory. In
, download Tomcat:
# cd /opt && wget http://apache.panu.it/tomcat/tomcat-8/v8.5.11/bin/apache-tomcat-8.5.11.tar.gz
Next, extract the Tomcat archive.
# tar xzvf apache-tomcat-8.5.11.tar.gz
Rename the extracted folder “tomcat”:
# mv apache-tomcat-8.5.11 tomcat
Then, change the owner to the ‘tomcat’ user, and make all the files in the bin directory executable. To accomplish this, execute the following commands:
# chown -hR tomcat:tomcat tomcat # chmod +x tomcat/bin/*
Next, you’ll need to define $CATALINA_HOME, which is an environment variable pointing to the base path of the Tomcat installation. In the
write:
and reload the file:
# source ~/.bashrc
Testing Apache Tomcat
In
there is a script,
. This starts and checks Tomcat. So, executing:
# $CATALINA_HOME/bin/startup.sh
you should see the following output:
Using CATALINA_BASE: /opt/tomcat Using CATALINA_HOME: /opt/tomcat Using CATALINA_TMPDIR: /opt/tomcat/temp Using JRE_HOME: /usr/lib/jvm/java-8-oracle/jre Using CLASSPATH: /opt/tomcat/bin/bootstrap.jar:/opt/tomcat/bin/tomcat-juli.jar Tomcat started.
Make sure that the last line is “Tomcat started.”; this means that Tomcat is correctly installed.
Tomcat uses the port 8080, so check that everything is okay:
# netstat -plntu | grep 8080
Result should be like this one:
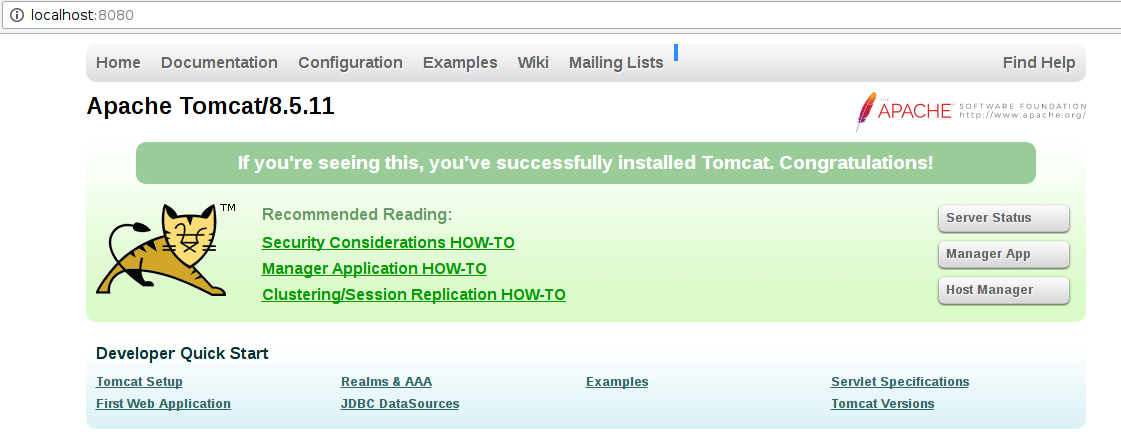
With your browser, go to the URL:
You should see the following page:
If you see this page it means that Tomcat is up and running correctly.
To shut down Tomcat, use this script:
# $CATALINA_HOME/bin/shutdown.sh
Create a systemd service
Once you have shut down Tomcat, in the systemd system directory, create a new file:
# $EDITOR /etc/systemd/system/tomcat.service
Paste the following configuration:
[Unit] Description=Apache Tomcat 8 Servlet Container After=syslog.target network.target [Service] User=tomcat Group=tomcat Type=forking Environment=CATALINA_PID=/opt/tomcat/tomcat.pid Environment=CATALINA_HOME=/opt/tomcat Environment=CATALINA_BASE=/opt/tomcat ExecStart=/opt/tomcat/bin/startup.sh ExecStop=/opt/tomcat/bin/shutdown.sh Restart=on-failure [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save and exit.
Now, use systemd to start the Tomcat service and then add its service to start at boot time. The commands are:
# systemctl daemon-reload # systemctl start tomcat # systemctl enable tomcat
Now Tomcat is running on port 8080.
Configure users
This next step is necessary because we can’t access the site-manager dashboard. So:
# $EDITOR /opt/tomcat/conf/tomcat-users.xml
Under line 43, paste the following content:
<role rolename="manager-gui"/> <user username="admin" password="password" roles="manager-gui,admin-gui"/>
Next, edit the
file.
# $EDITOR /opt/tomcat/webapps/manager/META-INF/context.xml
Here, comment the following lines:
<Context antiResourceLocking="false" privileged="true" > <!-- <Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.RemoteAddrValve" allow="127\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+|::1|0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1" /> --> </Context>
Save, exit and restart Tomcat:
# systemctl restart tomcat
Conclusion
That’s all! Now, you can go to
, which is the manager dashboard.
From now on, you can do everything through your browser. Tomcat 8.5 is running on your Debian 8 server!